Aerospace

Agriculture & Biosystems

Biomedical

Chemical

Civil

Computer Science

Electrical

Environmental

Industrial

Manufacturing

Materials Science

Mechanical

Mining & Metallurgical

Nuclear

Petroleum
Project Management
Biomedical Engineering
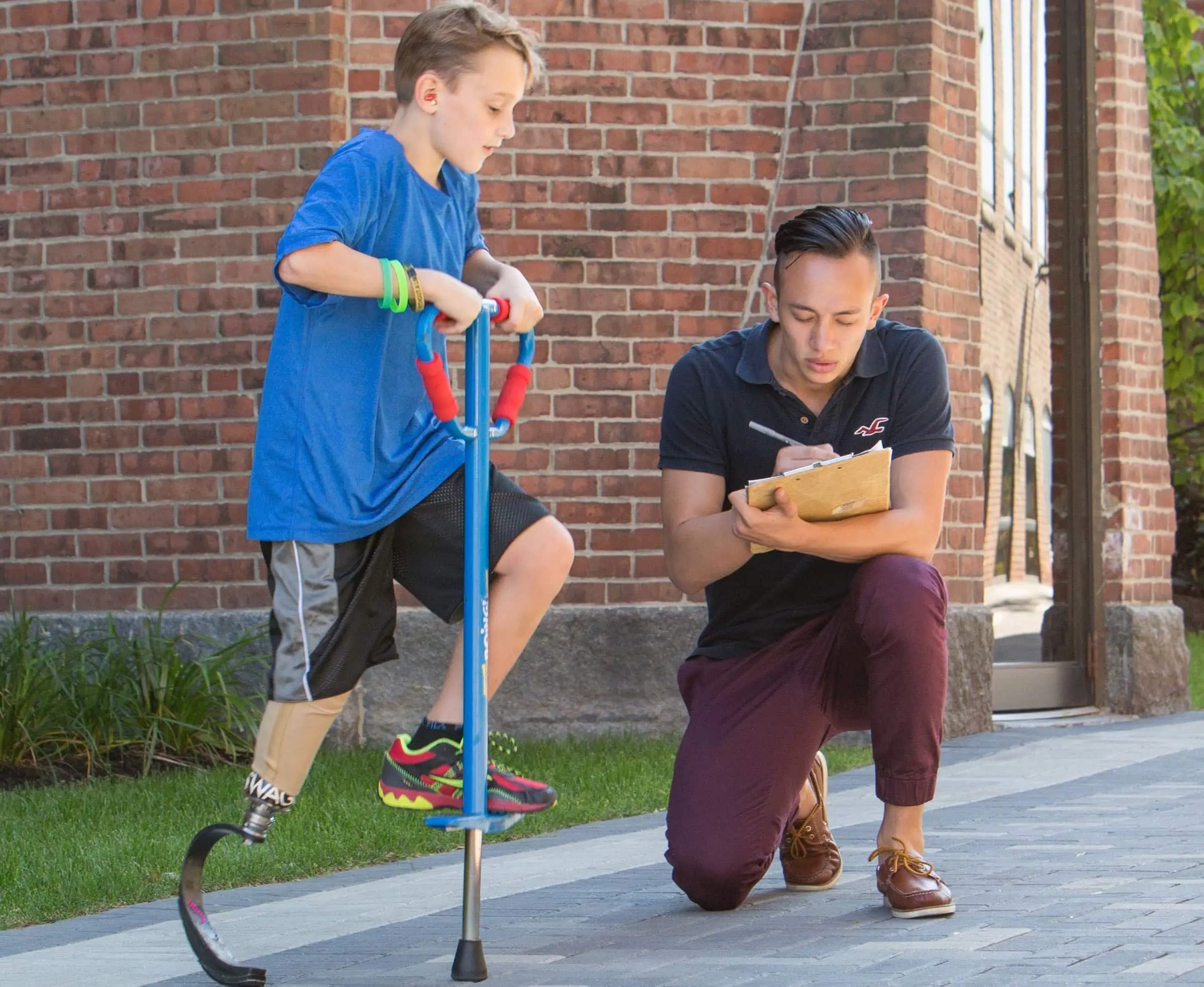

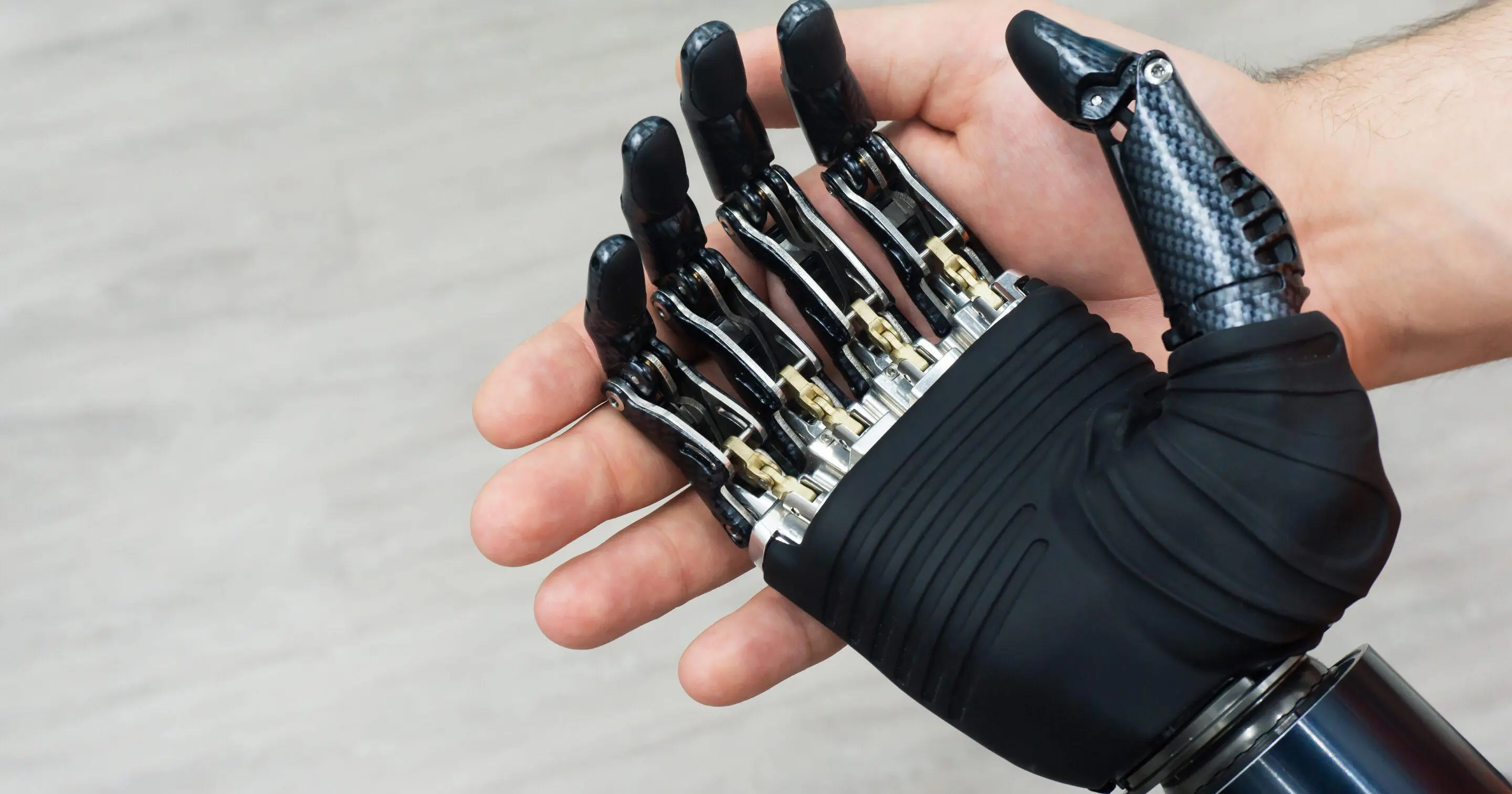
Where would modern medicine be without the contributions of biomedical engineering? Imagine hospitals operating without X-rays, ultrasound, EKGs, and the thousands of high-tech procedures and devices that diagnose conditions, sustain health, and fight disease. With a career in biomedical engineering, you’ll make a real difference in the lives of others. You might develop artificial lenses that restore sight to the blind, radiation treatments that fight cancer, or incubators that keep premature babies alive.
Biomedical Engineering Overview1
$92,620
Median salary
19,300
Number of jobs in 2020
6%
Expected job growth in next 10 years
Jobs and education
4-year degree:
- Grow tissues that help repair damage from heart attacks
- Develop new drug delivery methods and nano implants that target specific areas and don’t cause debilitating side effects.
- Design equipment that helps patients regain the ability to walk or create virtual reality systems that aid in limb mobility.
- Go on to pursue a medical degree in order to become a physician or surgeon.
2-year degree:
- Repair and maintain a variety of medical devices, including heart monitors, respiratory therapy devices, defibrillators, and medical imaging equipment.
- Operate and maintain the imaging machines, take the pictures, and verify that all safety protocols are being followed for both the patient and the medical staff.
- Pursue medical sales or become an equipment trainer for doctors and nurses.
References:
1. US Bureau of Labor Satistics
https://www.bls.gov/ooh/architecture-and-engineering/biomedical-engineers.htm